Synonym: von Recklinghausen disease.
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), a RASopathy, is one of the commonest autosomal
dominant inherited conditions (1 in 3000 births). NF1 is caused by mutations in a large
tumour suppressor gene encoding neurofibromin, a protein involved in the RAS/MAPK
signalling pathways responsible for cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation.
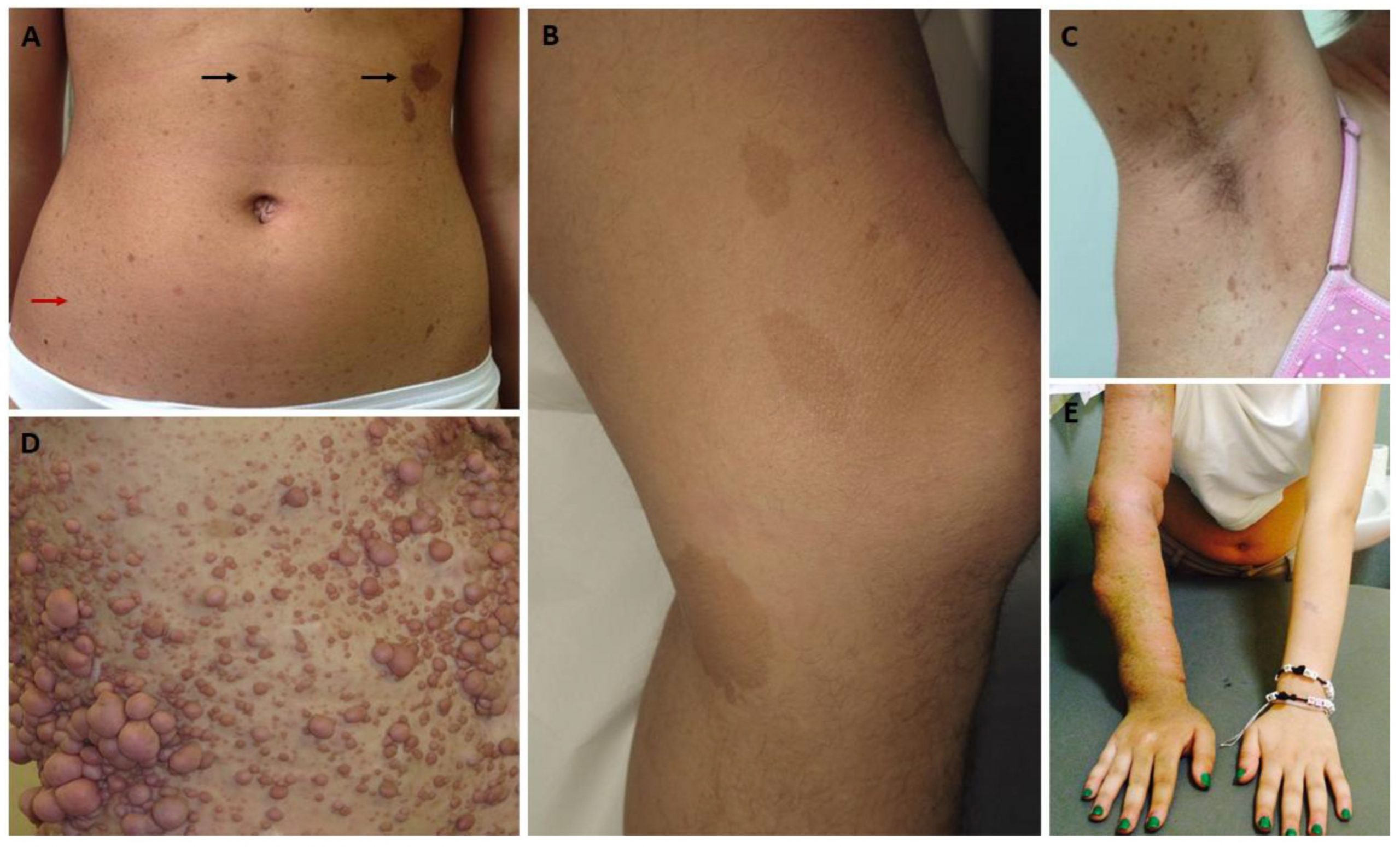
NFI is associated with other conditions. The diagnosis is clinical. There're some of the
causes of café au lait spots. Lipomas or tissue overgrowth in Proteus syndrome may
simulate the neurofibromas of NF1.
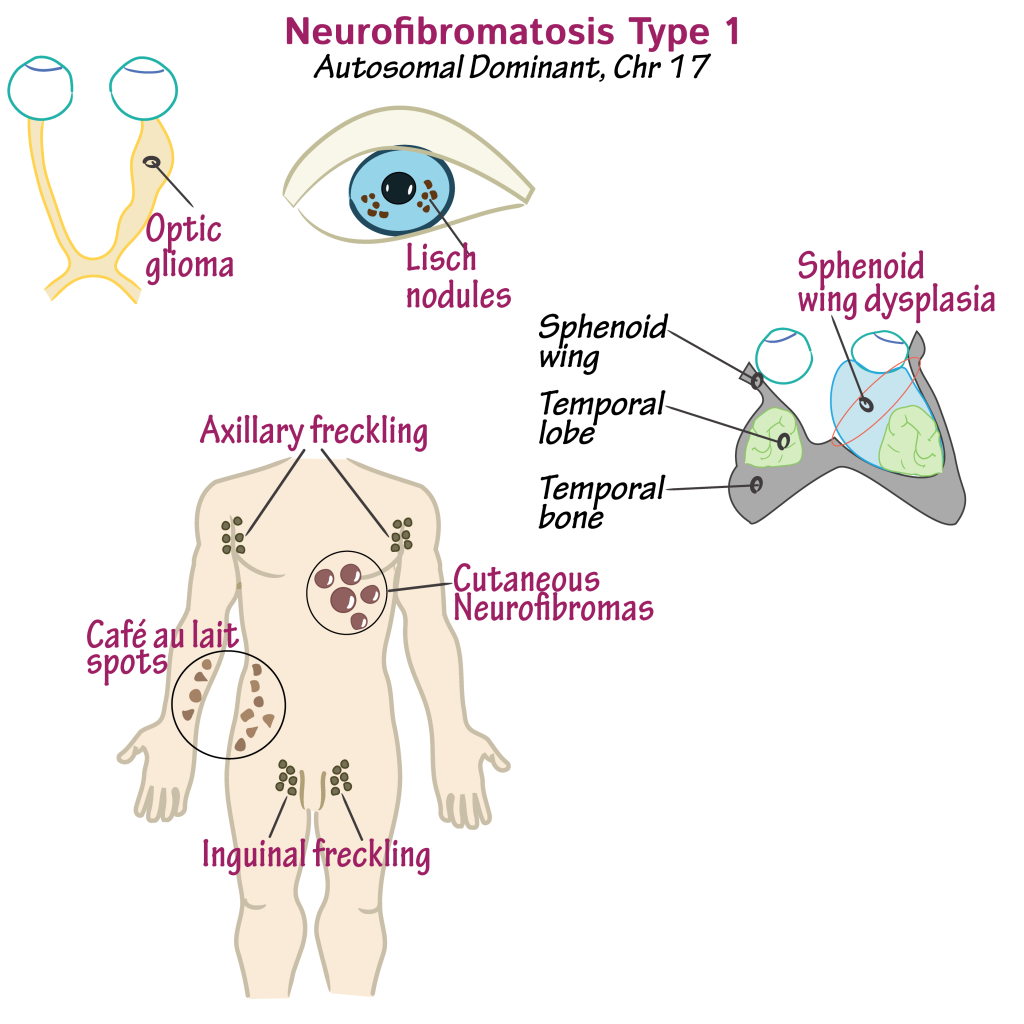
Diagnostic criteria:
Two or more of these clinical features establish the diagnosis:
• Six or more café au lait spots (macules or patches). Numbers increase in childhood.
Spots in prepubertal children >5mm in diameter, but post-puberty >15mm. Usually have
smooth outlines, but larger ones may be irregular. Intensity of colour varies, but most are
pale brown. Fade in adulthood.
• Axillary or inguinal freckles, 1–3mm in diameter, develop later than café au lait spots.
Freckling may also appear around the neck and in other skinfolds.
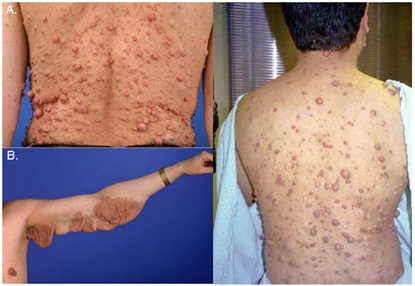
• Two or more neurofibromas of any type, or one or more plexiform neurofibroma.
Dermal neurofibromas also appear later than café au lait spots. Large numbers only
develop in adulthood. They may occur at any skin site but usually spare exposed skin
(e.g. face), except in severe cases. Apply gentle pressure to small neurofibromas, and
they sink down into the skin, ‘buttonholing’—a virtually pathognomonic sign.
Neurofibromas are soft and may become pedunculated. Patients may develop thousands
of disfiguring neurofibromas. Subcutaneous neurofibromas may involve major peripheral
nerves or nerve roots. Plexiform neurofibromas (usually congenital) track along nerves or
infiltrate subcutaneous tissues, and are associated with local hypertrophy of bone and soft
tissues. Overlying skin may be hyperpigmented, with increased hair growth
(hypertrichosis).
• An optic pathway glioma.
• Two or more Lisch nodules (melanocytic hamartomas of the iris). The yellowish-brown
nodules within the iris appear before neurofibromas and will confirm the diagnosis. They
are easier to see with a slit-lamp than with the naked eye, so refer to an ophthalmologist.
• Sphenoid wing dysplasia or thinning of the cortex of long bones, with or without
pseudarthrosis.
• First-degree relative with NF1 diagnosed by the presence of two or more of the above
criteria.