
1. Chlamydia is a common STD caused by the bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis. When undetected, the infection can travel up the reproductive organs and causes damage, resulting in infertility in severe cases. Chlamydia is known as a “silent” disease because about three quarters of infected women and about half of infected men have no symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they usually appear within 1 to 3 weeks after exposure. Symptoms might include abnormal discharge or a burning sensation when urinating. When the infection spreads from the cervix to the fallopian tubes (tubes that carry fertilized eggs from the ovaries to the uterus), some women may still have no signs or symptoms; others might have lower abdominal pain, low back pain, nausea, fever, pain during intercourse, or bleeding between menstrual periods. Men or women who have receptive anal intercourse may acquire chlamydial infection in the rectum, which can cause rectal pain, discharge, or bleeding.
Because Chlamydia infection is frequently asymptomatic and can lead to fertility problems in women if undetected, public health authorities in some countries have advised chlamydia screening for young and sexually active women–the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and the CDC strongly recommend that physicians routinely screen all sexually active women aged 25 years and younger, and other asymptomatic women at increased risk for infection from chlamydia.
2. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae.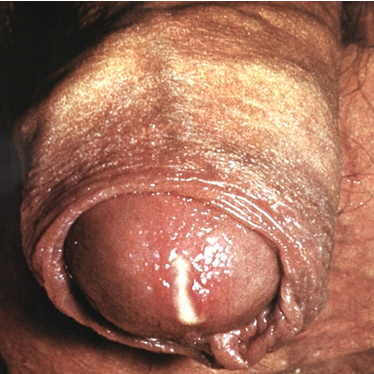 Gonorrhea is transmitted through sexual contact with the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus of an infected partner. Symptoms and signs usually appear two to five days after infection. In men, symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating, or a white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis, and sometimes painful or swollen testicles. In women, the symptoms of gonorrhea are often mild, nonspecific or absent, and sometimes can be mistaken for a bladder or vaginal infection. The initial symptoms in women include a painful or burning sensation when urinating, increased vaginal discharge, or vaginal bleeding between periods. Women with gonorrhea are at risk of developing serious complications from the infection, regardless of the presence or severity of symptoms.
Gonorrhea is transmitted through sexual contact with the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus of an infected partner. Symptoms and signs usually appear two to five days after infection. In men, symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating, or a white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis, and sometimes painful or swollen testicles. In women, the symptoms of gonorrhea are often mild, nonspecific or absent, and sometimes can be mistaken for a bladder or vaginal infection. The initial symptoms in women include a painful or burning sensation when urinating, increased vaginal discharge, or vaginal bleeding between periods. Women with gonorrhea are at risk of developing serious complications from the infection, regardless of the presence or severity of symptoms.
Symptoms of rectal infection in both men and women may include discharge, anal itching, soreness, bleeding, or painful bowel movements. Rectal infection also may cause no symptoms. Infections in the throat may cause a sore throat but usually cause no symptoms. When any person has typical symptoms of gonorrhea or chlamydia, even if the tests return negative, almost all doctors will treat with antibiotics, because the false negative rate is high. Since many people with gonorrhea also have Chlamydia, both infections are treated at the same time. Persons with gonorrhea should also be tested for other STDs. When one sexual partner is diagnosed with either chlamydia or gonorrhea, or it is strongly suspected, the other partner(s) should be treated as well even if they have no symptoms to prevent spread.
3. Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Syphilis is passed from person to person through direct contact with a syphilis sore during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Sores occur mainly on the external genitals, vagina, anus, or in the rectum. Sores also can occur on the lips and in the mouth. Syphilis infection has three stages.
The primary stage is manifested as a painless sore, or ulcer, on the body part where the bacterium enters. The sore lasts 3 to 6 weeks and resolves with or without treatment. However, without treatment, syphilis can reappear in the second stage.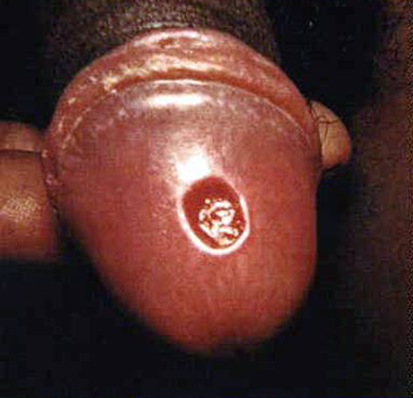
The secondary stage starts with a rash and/or sores on one or more areas of the body. The rash can appear from the time when the primary sore is healing to several weeks after the sore has healed. The rash is usually not itchy and may appear as red or reddish brown spots on palms and soles. Sometimes they are so faint they are not noted. Large, raised, gray or white lesions may develop in warm, moist areas such as the mouth, underarm or groin region. Other symptoms of secondary syphilis include fever, swollen lymph glands, patchy hair loss, weight loss, muscle aches, and fatigue. The symptoms of secondary syphilis will go away with or without treatment. Without appropriate treatment, the infection will progress to the latent and possibly late stages of disease.
The latent (hidden) stage of syphilis begins when primary and secondary symptoms disappear. Without treatment, the infected person can continue to have syphilis in their body even though there are no signs or symptoms. This latent stage can last for years. About 15% of people who have not been treated for syphilis develop late stage syphilis, which can appear 10–30 years after infection began. Symptoms of the late stage of syphilis include difficulty coordinating muscle movements, paralysis, numbness, gradual blindness, and dementia. In the late stages of syphilis, the disease damages the internal organs, including the brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints. This damage can result in death. (Source: http://www.cdc.gov/STD/syphilis/STDFact-Syphilis.htm)
Syphilis can be easily diagnosed by a blood test and is treatable by antibiotics.
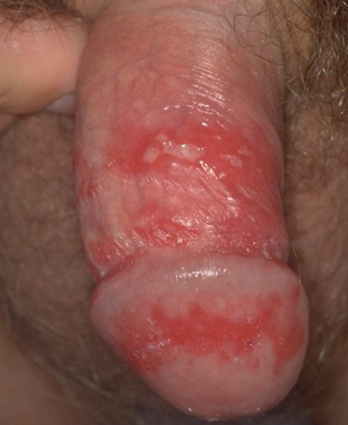 4. Genital Herpes is a sexually transmitted disease caused by two similar viruses, Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 and type 2. Most genital herpes is caused by HSV 2. The infection manifests as one or more blisters on or around the genitals or rectum. The blisters break and become tender ulcers (sores) that may take two to four weeks to heal. There may be fevers, swollen glands, and flu-like symptoms. Recurrent outbreaks are common, though they tend to be less severe and shorter than the first. Infection with HSV is life-long and follows a variable course of having no symptoms to few or frequent outbreaks.
4. Genital Herpes is a sexually transmitted disease caused by two similar viruses, Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 and type 2. Most genital herpes is caused by HSV 2. The infection manifests as one or more blisters on or around the genitals or rectum. The blisters break and become tender ulcers (sores) that may take two to four weeks to heal. There may be fevers, swollen glands, and flu-like symptoms. Recurrent outbreaks are common, though they tend to be less severe and shorter than the first. Infection with HSV is life-long and follows a variable course of having no symptoms to few or frequent outbreaks.
Most people with HSV 2 do not know that they are infected. Transmission can occur from an infected partner who does not have visible sores. Correct and consistent use of latex condoms reduces the risk of genital herpes, however, herpes infection can occur in areas not covered by the condom and is therefore transmissible even with condom use. Persons with visible herpetic sores should abstain from sexual activity with uninfected partners.
HSV-1 can cause genital herpes, but it more commonly causes infections of the mouth and lips, the so-called “fever blisters”. Genital herpes infection by HSV-1 is transmitted by oral-genital or genital-genital contact with a person who has HSV-1 infection.
Health care providers can diagnose herpes by visual inspection or by laboratory testing. There are no treatments that can cure herpes, but antiviral medications can shorten the course of the outbreak. In addition, daily suppressive therapy for symptomatic recurrent herpes can reduce outbreaks and transmission to partners.
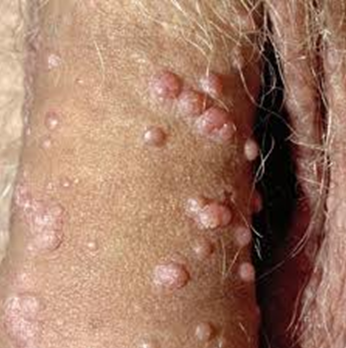 5. Human papilloma virus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus worldwide. Certain types of HPV cause genital warts, while others are associated with cervical and anal cancers. Cervical cancer is the number 2 cause of cancer deaths in women around the world. HPV can also infect the mouth and throat. Most people carrying HPV are asymptomatic, however, they still can transmit the virus to their partners.
5. Human papilloma virus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus worldwide. Certain types of HPV cause genital warts, while others are associated with cervical and anal cancers. Cervical cancer is the number 2 cause of cancer deaths in women around the world. HPV can also infect the mouth and throat. Most people carrying HPV are asymptomatic, however, they still can transmit the virus to their partners.
The genital warts usually appear as a small bump or groups of bumps in the genital area. They can be small or large, raised or flat, or shaped like a cauliflower. If left untreated, they might go away, remain unchanged, or increase in size or number. Warts are usually diagnosed clinically.
Vaccines are available against some types of HPV. Gardasil is a vaccine against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18, which can protect against approximately 70% of cervical cancers and 90% of genital warts. The vaccine is recommended for both males and females age 9 to 26 and is a 3-shot series given over 6 months.
6. Hepatitis B is caused by a virus that infects the liver. Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The hepatitis B is transmitted through sex, blood, and mother to child. This virus is highly endemic in Vietnam though the incidence may have decreased since the institution of national childhood vaccination program. If infected as an infant, about 90% will become chronically infected, therefore it is important for pregnant women to be tested and treated for hepatitis B.
Acute hepatitis B can range from asymptomatic to life-threatening. Symptoms may include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, jaundice and icterus (skin and eye having a yellowish hue. Following acute hepatitis, about 80% of people will clear the virus and develop immunity. The rest may go on to have chronic or lifelong hepatitis. Complications from chronic hepatitis B include cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Treating hepatitis B significantly reduces rates of hepatocellular carcinoma.
The best protection against this virus is vaccination. It’s a 3 shot series, which could be given over 4 to 6 months. A 4 shot series over 12 months (3 shots over 2 months then booster shot at 12 months) is also approved. According to the CDC (Center for Disease Control and Prevention – The US government’s authoritative source on infectious diseases) periodic testing to determine antibody levels after routine vaccination in immunocompetent persons is not necessary, and booster doses of vaccine are not currently recommended.
7. HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. There are 32 million people in the world infected with HIV currently. According to the Vietnam Administration for HIV/AIDS control, in 2012 there are 210,000 people living with HIV in Vietnam, for a prevalence of about 0.25%. Although the epidemic in Vietnam is concentrated in drug users and sex workers, the rate of transmission through heterosexual sex is increasing.
HIV is transmitted through sex, blood, and mother-to-child. The virus is concentrated in blood, semen, breast milk, and vaginal fluid. It is not found in significant amount in saliva or urine (but urine may be contaminated with semen). HIV is not transmitted through mosquito bites.
HIV has a uniquely long latency period of 5-10 years, during which time the patient has no or minimal symptoms. For this reason many people do not know that they are infected and can transmit HIV to others. The virus gradually destroys the immune system, and eventually patient will develop infections, especially pneumonia, meningitis, tuberculosis, and other problems. This stage is called AIDS.
Dr. Doanh Lu is an American Board Certified in Infectious Diseases, and has had many years of experience treating HIV. She was trained at one of the largest HIV centers in the US. Following her infectious disease training, she worked for the Harvard Medical School AIDS program in Vietnam and has expertise in treating adult, children, and pregnant women with HIV.
