- News
- 06/05/2019
- 2
*** Where does it occur?
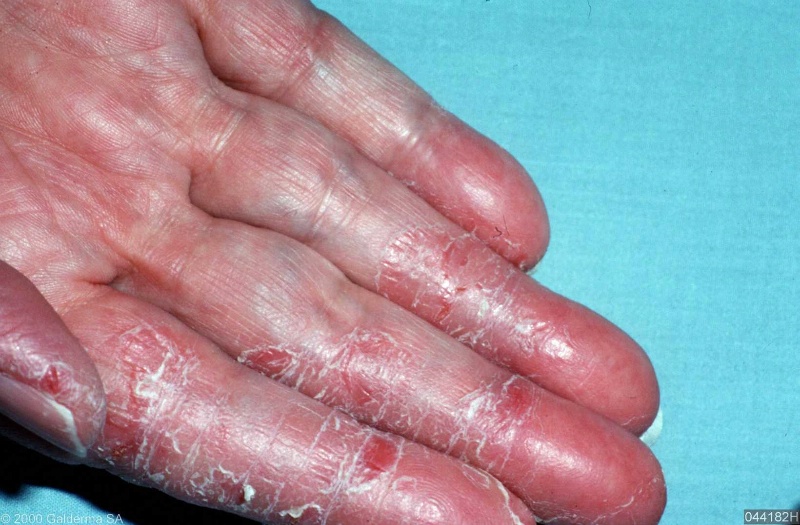
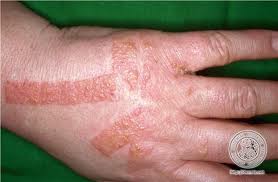
When it occurs on the hands, it can also have small blisters along the sides of the fingers or on the palms. The hands may become dry and painful with splitting and cracking on the palms or around the fingers.
*** What causes it?
Constant wetting and drying of hands, plus the increased contact with soaps, detergents and other irritants when looking after young babies may cause hands to become irritated. If a person has a tendency to develop dermatitis already, they will be more likely to develop it on the hands at this time.
Occasionally, a true allergy to a chemical that is being used may cause hand dermatitis. But the majority of dermatitis affecting the hands is not due to allergy.
Getting run down, tired and under stress will make dermatitis worse.
Scratching may lead to breaking the surface of the skin and the dermatitis may become infected. Hand dermatitis can be worse during the winter with cold weather causing low humidity and drying out the skin. Contact with other products which dry the skin such as solvents including turpentine, kerosene, petrol, household goods, gardening and food preparation will make hand dermatitis more of a problem.
*** How is it treated?
A major part of the management of hand dermatitis is in avoiding things that irritate the skin. This includes minimising hand washing and contact with soap, detergents and other solvents or irritants. PVC cotton lined gloves are useful for heavier work. For fine work cotton gloves under rubber gloves may be used. Rubber gloves alone may irritate the skin due to sweating.
Rings may trap soap, water and other chemicals underneath them and should be removed before washing hands with soap or after doing housework. Skin under the rings should be carefully dried. The ammonia in wet nappies can also cause irritation. Nappies should be handled with tongs or with gloves to avoid direct contact with the hands. Water alone can act as an irritant by washing away protective oils on the skin.
Moisturisers such as sorbolene cream, aqueous cream or mulsifying ointment can be used instead of soap. They should also be applied to the skin frequently during the day as a moisturiser and especially after washing. When the dermatitis is active, cortisone creams or ointments prescribed by a doctor may be necessary to settle the inflammation. Treatment of any infection may also require antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
Once the dermatitis has settled, the cortisone creams are stopped. To prevent dermatitis returning regular application of moisturisers and avoiding irritants should be continued. Occasionally, PATCH TEST by a dermatologist may be necessary to determine whether a true allergy to a chemical is occurring. If allergy does occur, then it is important to avoid contact with the chemical.
*** Important Points
• Remember that water alone can act as an irritant
• Minimise hand washing
• Avoid direct contact of skin with soap, detergents, shampoos and other irritants
• Use cotton-lined gloves, rather than rubber gloves alone, when working with water and other irritants
• Use moisturisers such as sorbolene or aqueous cream or emulsifying ointment often
• Use moisturisers especially after washing hands
• Cortisone creams and ointments prescribed by a doctor should only be used when the dermatitis is present