- News
- 06/05/2019
- 2
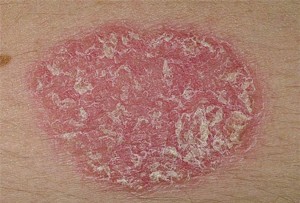
Psoriasis is a common skin disorder that forms thick, red, bumpy patches covered with silvery scales. They can pop up anywhere, but most appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
Psoriasis can’t be passed from person to person. It does sometimes happen in members of the same family.
It usually appears in early adulthood. For most people, it affects just a few areas. In severe cases, it can cover large parts of the body. The rashes can heal and then come back throughout a person’s life.
Symptoms
Psoriasis starts as small, red bumps, which grow bigger and form scales. The skin appears thick but may bleed easily if you pick or rub off the scales.
Rashes may itch and cause pitted, cracked, crumbly, or loose nails.
How Do I Know If I Have Psoriasis?
If you have a rash that isn’t healing, see your doctor.
Causes
No one knows the exact cause of psoriasis, but experts believe that it’s a combination of things. Something wrong with the immune system causes inflammation, triggering new skin cells to form too quickly. Normally, skin cells are replaced every 28 to 30 days. With psoriasis, new cells grow every 3 to 4 days. The buildup of old cells being replaced by new ones creates those silver scales.
Some things that can trigger outbreaks are:
- Cuts, scrapes, or surgery
- Emotional stress
- Strep infections
Treatment
Luckily, there are many treatments. Some slow the growth of new skin cells, and others relieve itching and dry skin. Your doctor will select a treatment plan that is right for you based on the size of your rash, where it is on your body, your age, your overall health, and other things. Common treatments include:
- Steroid creams
- Moisturizers for dry skin
- Coal tar (a common treatment for scalp psoriasis; available in lotions, shampoos, and bath solutions)
- Vitamin D cream (a strong kind ordered by your doctor; vitamin D in foods and pills has no effect)
- Retinoid creams
v Treatments for moderate to severe cases of psoriasis include:
- Light therapy. A doctor uses ultraviolet light to slow the growth of skin cells. PUVA is a treatment that combines a medicine called psoralen with a special form of ultraviolet light.
- Methotrexate. This drug can cause liver disease and lung problems, so it’s only for serious cases. Doctors closely watch patients. You may have to get chest X-rays and liver biopsies.
- Retinoids. These pills, creams, and gels are a class of drugs related to Vitamin A. Retinoids can cause serious side effects, including birth defects, so they’re not recommended for women who are pregnant or planning to have children.
- Cyclosporine. This drug, made to suppress the immune system, may be taken for serious cases that do not respond to other treatments. It can damage the kidneys and raise blood pressure, though, so your doctor will closely watch your heath while you take it.
- Biologic treatments. These work by blocking the body’s immune system from “kick-starting” a disease such as psoriasis.
Is There a Cure?
There’s no cure, but treatment greatly reduces symptoms, even in serious cases.